I. Introduction
In traditional finance, options trading has long been a popular financial instrument for investors seeking to hedge against market volatility or generate additional income through speculation. With the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), options trading has also emerged as a promising area for growth within the cryptocurrency market. DeFi options allow users to trade options contracts using blockchain technology, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks or brokers. This creates a more transparent, accessible, and efficient trading environment that is open to anyone with an internet connection and a cryptocurrency wallet.
If we work backwards and look at what the traditional markets tell us about the relationship between options and derivatives activity, we can forecast where the DeFi options space will end up.
DeFi has gained significant traction in recent years as a result of its ability to provide financial services without intermediaries. DeFi protocols offer a wide range of services, including borrowing, lending, staking, and trading. Options are financial instruments that provide the holder with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price and date. Options can be used for hedging, speculation, and income generation. In the DeFi space, options trading has been enabled by automated market maker (AMM) protocols.
AMM protocols are designed to provide liquidity for trading by using a pricing curve algorithm to adjust prices based on the demand and supply of assets. Unlike traditional order book-based trading, AMMs are more decentralized and do not rely on centralized entities to match buyers and sellers. However, the current state of options trading in DeFi is still relatively nascent, with a limited number of platforms offering options trading on a select number of cryptocurrencies. Additionally, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed in order for DeFi options to achieve wider adoption, such as ensuring accurate pricing, minimizing the risk of impermanent loss for liquidity providers, and improving user experience.
Nevertheless, the potential benefits of DeFi options are significant, including increased liquidity, lower fees, and more accessible trading opportunities for a wider range of investors. As DeFi continues to grow and mature, it is likely that the options market will become an increasingly important and lucrative area within the ecosystem.
Currently, the number of protocols offering options trading in DeFi is quite modest and the volume of transactions has not attracted cash flow from retailers and is far from institutions. This article will introduce the 2nd largest options trading platform in DeFi, at the time of writing, Lyra Finance
II. What is Lyra Finance?
Lyra is an option trading protocol built on layer 2 scaling solutions of Ethereum, such as Arbitrum and Optimism. Lyra provides a new and innovative approach to options trading in DeFi by allowing traders to buy and sell options on cryptocurrencies against a pool of liquidity. This article will only focus on analyzing Lyra's products, the options trading mechanism will be covered in other articles.
Lyra's unique approach to options trading in DeFi is based on an automated market maker (AMM) model. This model pools liquidity from external liquidity providers and allows traders to buy and sell options at a price determined by an algorithm that is based on supply and demand.
Lyra has two key user groups: liquidity providers and options traders. Liquidity providers supply liquidity to the protocol, which is used to offer options trading to traders. In return for their liquidity, providers receive a portion of the trading fees generated by the protocol. Options traders, on the other hand, use the Lyra protocol to buy and sell options on cryptocurrencies. Traders can use Lyra's easy-to-use interface to access a range of options contracts, such as call and put options, with varying strike prices and expiration dates.
How Does Lyra Work?
Lyra's automated market maker (AMM) functions as a liquidity pool that allows users to trade options on cryptocurrencies. The AMM is made up of a smart contract that uses an algorithm to determine the price of each option contract based on the supply and demand of the pool. When a trader buys an option, they are essentially buying a right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell an underlying asset, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, at a predetermined price and date. If the trader chooses not to exercise their option, they lose the premium paid.
In Lyra's ecosystem, liquidity providers play a crucial role in supplying the pool with liquidity. They can contribute any amount of cryptocurrency to the pool and receive a portion of the trading fees generated by the protocol in return. The amount of fees earned by liquidity providers is proportional to the amount of liquidity they supply to the pool. Options traders, on the other hand, use the Lyra protocol to buy and sell options on cryptocurrencies. They can choose from a range of options contracts with varying strike prices and expiration dates.
To ensure the accuracy of option prices and minimize the risk of impermanent loss for liquidity providers, Lyra uses an algorithmic pricing mechanism that takes into account the supply and demand of the pool. This mechanism ensures that the price of each option contract accurately reflects the market price of the underlying asset. Additionally, Lyra's AMM model minimizes the risk of impermanent loss for liquidity providers by adjusting the price of each option contract in real-time based on market conditions. If the price of the underlying asset increases or decreases, the price of the option contract will also adjust to reflect this change.
III. Benefits of an Options AMM vs Options Vault
In the DeFi options market, two primary models have emerged: options automated market makers (AMMs) and options vaults. While both models offer their own unique benefits and drawbacks, understanding the differences between them can help investors make more informed decisions when trading options.
One of the primary benefits of an options AMM, such as Lyra, is that it provides a more efficient and flexible trading environment. With an AMM, traders can buy and sell options against a pool of liquidity, rather than waiting for counterparties to take the other side of their trade. This can result in faster execution times, lower fees, and more accessible trading opportunities for a wider range of investors.
Another benefit of an options AMM is that it can help ensure more accurate pricing for options contracts. AMMs use complex mathematical algorithms to price options based on current market conditions and liquidity, which can help prevent mispricings and ensure that traders are receiving fair market value.
However, one potential hindrance of an options AMM is the risk of impermanent loss for liquidity providers. When providing liquidity to an AMM, liquidity providers are exposed to fluctuations in the price of the underlying asset, which can result in losses if the price moves against them. While Lyra has implemented several measures to mitigate this risk, including dynamic fees and virtual balances, it remains a concern for some investors.
In contrast, options vaults, such as Opyn and Hegic, offer a different set of benefits and drawbacks. Options vaults allow investors to write options contracts and earn premiums for doing so. This can be an attractive option for investors who are looking to generate additional income or hedge against market volatility. However, options vaults can also be more complex and less flexible than AMMs, and may not offer the same level of accuracy in pricing options contracts.
IV. Lyra vs Others
Lyra operates in a highly competitive market with several other DeFi options trading protocols vying for users' attention. Some of Lyra's most significant competitors include Hegic, Opyn, and Dopex.

One key differentiator between Lyra and its competitors is its use of layer 2 scaling solutions, such as Arbitrum and Optimism. In contrast, Hegic and Opyn both rely on Ethereum's layer 1 infrastructure, which can lead to slower and more expensive trading. Dopex, on the other hand, uses a combination of layer 1 and layer 2 solutions, but does not offer the same flexibility and efficiency as Lyra's AMM model.
Lyra's AMM model also sets it apart from some of its competitors. Hegic and Opyn both use order book models, which can be more complicated and less efficient than AMMs. Dopex focuses on building trading strategies with automated vaults. Of course, each protocol is geared towards a different user base, Dopex's Options Vaults aim to get the yield to vanilla yield farming and staking by providing access to options premium. Protocols like Ribbon, Dopex are able to offer their users sustainable yield by bundling complex option trading strategies into a single 1-click deposit platform, known as a kind of structured product.
Meanwhile, Lyra is the only decentralized options exchange right now that can facilitate the sale of options back into a liquid market via the AMM - alternatives only allow the option holder to expire the options early (american style options) or wait for the option to mature to the final expiration date. This is an important mechanism for traders, as more views can be expressed by buying and selling options instantly with liquidity, such as harvesting volatility risk premiums.
While Lyra has several strengths compared to its competitors, one potential weakness is the size of its liquidity pool relative to some of its competitors. Hegic, for example, boasts a significantly larger liquidity pool, which could limit the trading volume and liquidity available on Lyra during times of high market volatility. At the time of writing, Lyra is in second on the options TVL rankings, accounting for $33.41M, behind the leading - Opyn with $40.4M.
Overall, Lyra's use of layer 2 scaling solutions, flexible AMM model, and focus on accurate pricing and risk mitigation make it a strong competitor in the DeFi options market. However, the protocol will need to continue to build out its liquidity pool and expand its product offerings to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
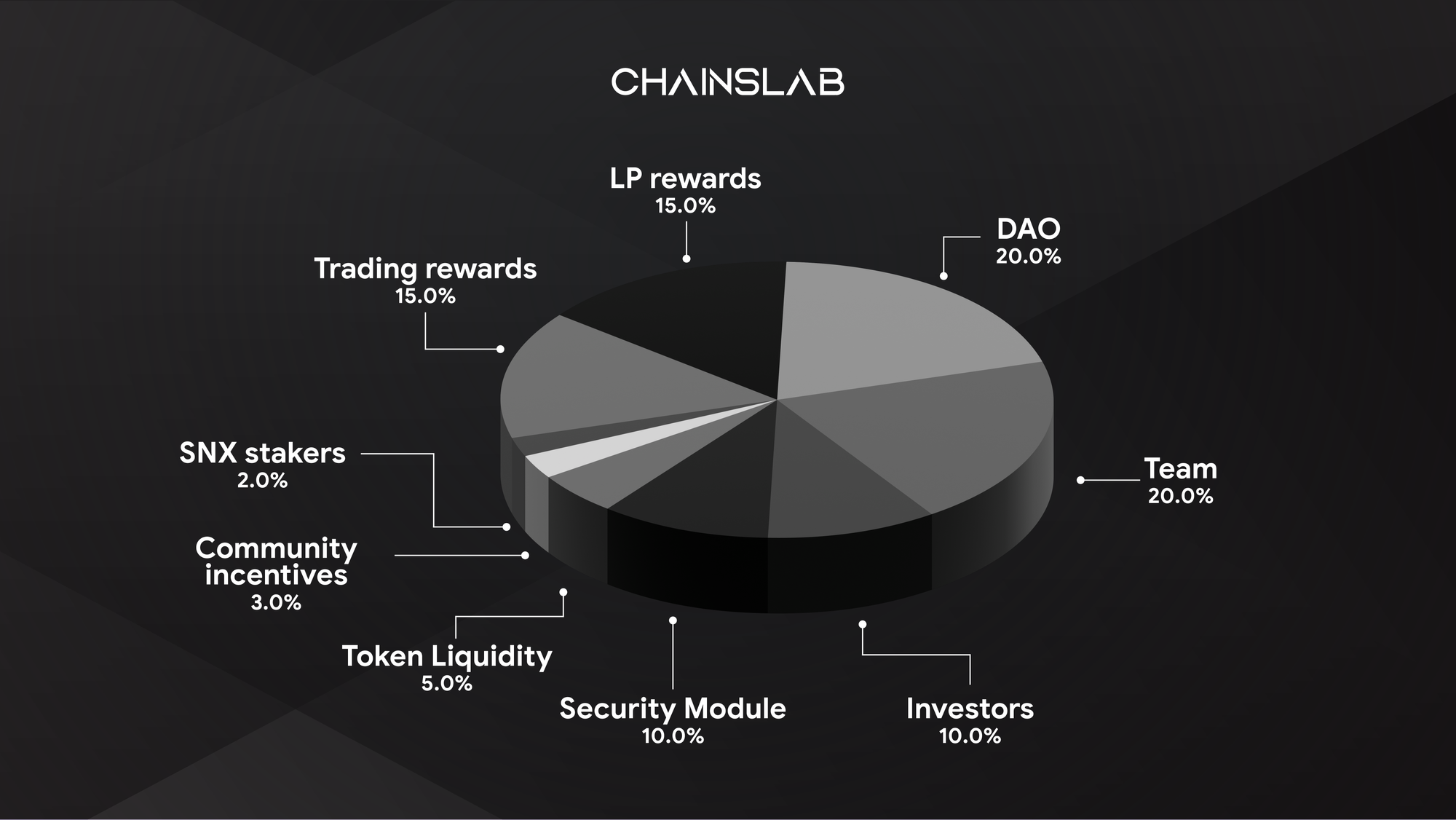
V. LYRA Tokenomics
With 1 billion LYRA tokens minted, LYRA was earned by traders, LPs and the community over a 6 week period leading up to the token unlock called ‘Ignition’. After January 7th there will be three use cases for the token.
- Can be staked in the Security Module (SM)
- Can be used to vote on Council elections
- Can be staked in the LYRA-ETH Uniswap pool to earn LYRA rewards
Beyond these functions, the most powerful path for the LYRA token is to build an emissions and staking system that deeply integrates token functionality with trading volumes and market liquidity. This path will drive tokens into the hands of community members, traders, and LPs who are long-term aligned with the protocol. Soon, users will be able to stake their LYRA in return for xLYRA which acts as a rewards boost for trading and liquidity providing. The idea for this implementation is inspired by Curve’s veCRV token.
VII. Some Evaluation on Lyra
Lyra is going for the options-trading sub-sector, so hopefully they can become as big a name as GMX in that regard, as the first-mover grabs. Lyra does have a good chance of catching up to its two main competitors in Dopex and Opyn in terms of volume and TVL, especially seeing as it’s the first protocol to integrate on the two greatest layer 2s, so far, and is the only protocol out of the remaining utilizing an option automated market maker (AMM). The use of an automated market maker (AMM) system also provides users with easy and efficient access to liquidity pools, making it easier to trade options with minimal slippage.
One of the notable benefits of Lyra is the ability for liquidity providers to earn fees by providing liquidity to the platform. This incentivizes participation and helps ensure that there is sufficient liquidity for traders to engage in trading activities. Furthermore, the use of LYR token for governance, rewards, and fees provides an additional layer of incentives for users to participate in the platform and contribute to its growth.
However, there are also some potential hindrances to Lyra's growth. The current state of DeFi options trading is still relatively nascent, with limited adoption and a small user base. Additionally, the use of options AMMs as opposed to options vaults may not be suitable for all types of traders, particularly those with large positions or advanced trading strategies.
