I. Introduction.
2022 was and will be a tumultuous, eventful yet unforgettable year for the Blockchain industry. We have eyewitnessed the collapse of Do Kwon's Terra and the fall of Su Zhu's Three Arrow Capital, but the biggest thing that happened and worth mentioning is The Merge. It is the replacement of the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism with the Proof-of-Stake mechanism on Ethereum, the second largest blockchain in the world. This is not only a big milestone for Ethereum but the whole blockchain industry since it is wiping off the famous POW mechanism and also the war of ETH miners.
Leaving aside the controversy over whether this is the right path for Ethereum development or not (which will be covered in another article), let's take a look at its biggest impact on the industry. As for now, due to its problem of maintenance and scalability, the famous Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism is only used by a handful of Layer-1s.
Kadena is one of the few players that is still playing the POW game. Launched 6 years ago, in 2016, completed multiple funding rounds, and received plenty of support from the big names in the industry, still, this blockchain remained in a low-key mode until now.
The name Kadena popped up on September 13, 2022, when Bitmain (a privately owned company in China, that designs application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chips for bitcoin mining) announced a new line of exclusive KDA miners - Antminer KA3. Coincident or not, this announcement took place just right before the Merge, which can translate into a large shift of ETH miners to other networks.
What is Kadena and what future hold for this project? Well, this article was born to answer that.
II. What Is Kadena?
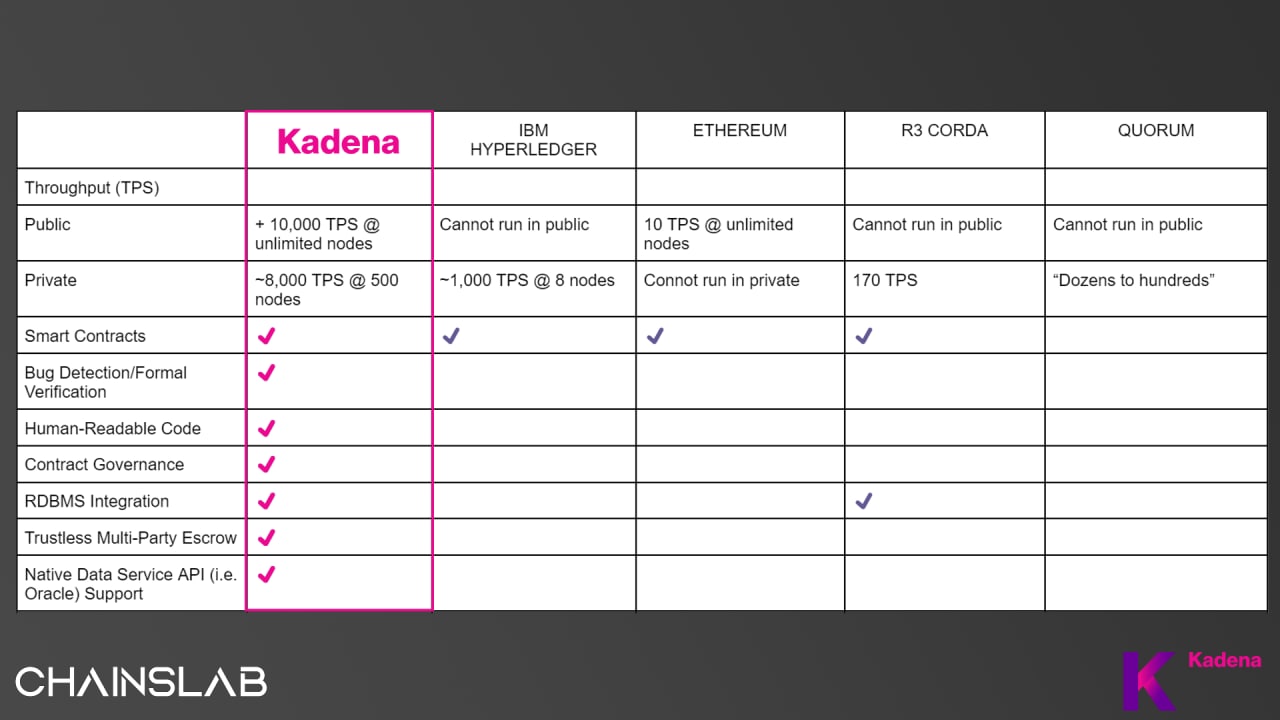
Kadena is the industry’s only scalable layer-1 Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchain. The principal feature that drives Kadena is scalability, which enables Kadena to deliver infrastructure-grade performance for any blockchain project. Along with its own smart contract language - Pact, Kadena’s platform provides the world the tools and environment to turn ideas and ambitions into reality.
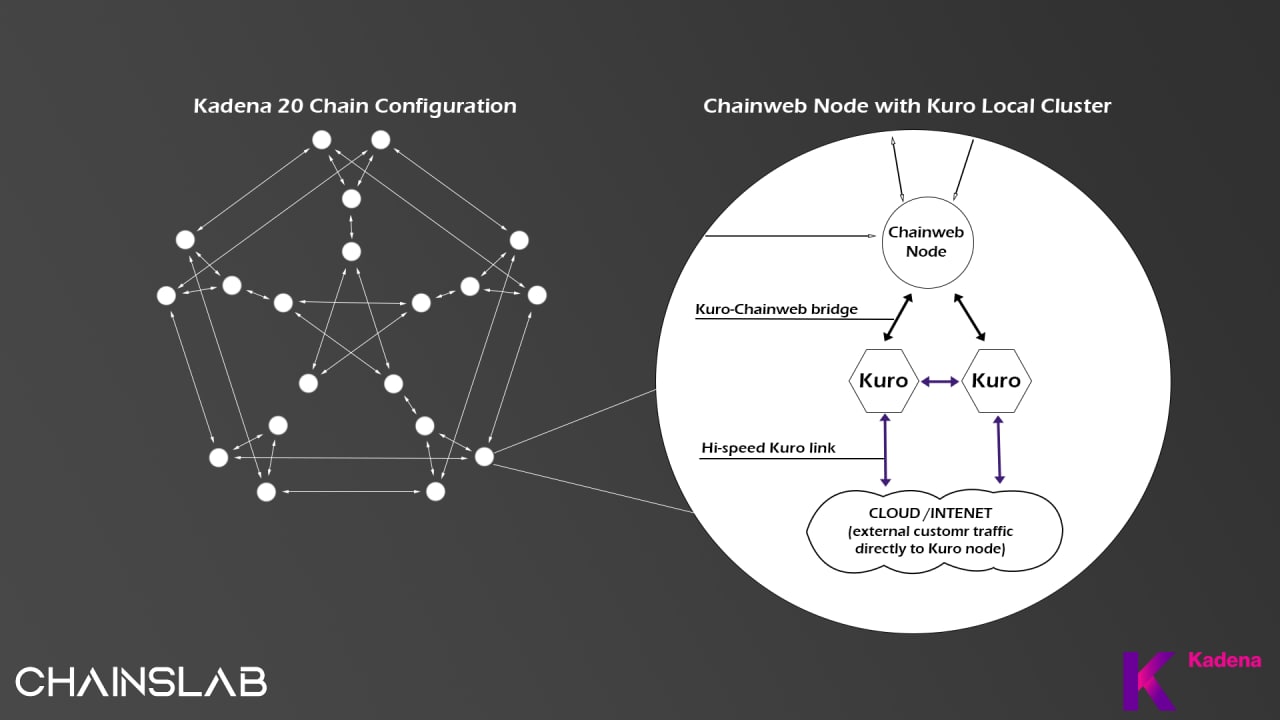
Kadena is the world’s first scalable Proof-of-Work blockchain using a sharding approach. The Kadena network itself operates across multiple interweaving blockchains. This includes a public layer-1 called ChainWeb, and a private layer-2 network called Kuro. Furthermore, the third element of Kadena is its open-source programming language called Pact. These will be explained in the section below.
III. Will It Moon?
The cake is getting smaller and smaller, it is even harder to survive in the niche when new generation blockchains are constantly being researched and released. Thus, there are always 2 questions:
- What determines the difference between Kadena and other blockchains?
- Will the PoW scalability dilemma problem on Kadena be completely solved?
Until now, the biggest strength of Kadena is probably relying on fairly strong backers, especially the support from Bitmain. Ironically, Bitmain has never been known for helping ecosystems achieve success, but the bright thing is they do bring a new flow of money to the Kadena ecosystem.
In a bear market, surviving is something more important than developing or scaling. A fresh capital stream (in this case, the Bitmain stream) will significantly help Kadena to survive. Keep in mind that, alpha is born in the bear market.
In fact, the PoW mechanism still has some limitations, though Kadena knows how to improve and bring the strength of the network to mass adoption.
The Proof-of-Work mechanism comes with both up and downsides, but it was and will be one the Kadena's competitive advantages. When Kadena knows how to minimize the downsides, we can enjoy the advance of POW, including:
- Safer and smarter contracts with Pact programming language.
- “Human-readable" language to execute smart contracts with correctness.
- All functions that are executable by computers are available in the language.
- Upgradable smart contracts.
- ...
IV. Mechanism of Kadena.
TL; DR.
- Kadena is a PoW layer 1 blockchain with the idea of multiple parallel blockchains to address issues of scalability powered by its unique architecture.
- This multi-chain architecture is called Chainweb that uses sharding to process up to 480k TPS.
- Kuro is a private chain designed for commercial use and brings smart contracts and privacy features to the chain.
- Pact smart contract is a new programming language developed by the Kadena team.
Kadena is a multi-chain network comprising braids of numerous “Bitcoin-like” chains. But first, we need to know the problems of current blockchains to see how Kadena can solve them:
- Security & Decentralization: The majority of blockchains today use many other consensus mechanisms with more advantages to replace the traditional POW mechanism originally of Bitcoin. However, there must be a trade-off between both.
- Scalability: The main problem with current blockchains is the ability to scale the system to meet increasing transaction needs and adoption. Specifically, the ability to process many transactions at the same time, helping the system not to be congested while reducing gas fees.
Initially, the Kadena network had ten chains during the launch. However, the scalable infrastructure means that Kadena can add further chains to infinitely grow due to its adoption and demand. The multi-chain architecture increases throughput and security with additional chains. In 2020, Kadena grew from ten to twenty chains throughout the year, doubling the network throughput, proving the network’s ability to scale. The team planned on expanding this further to 100 chains within the following twelve months, but no development so far (at the time writing). In the case of 100 active chains, the team estimates Kadena will be capable of processing 1,000 to 10,000 transactions per second (TPS) per chain. Thus, the network could process one million TPS in total.
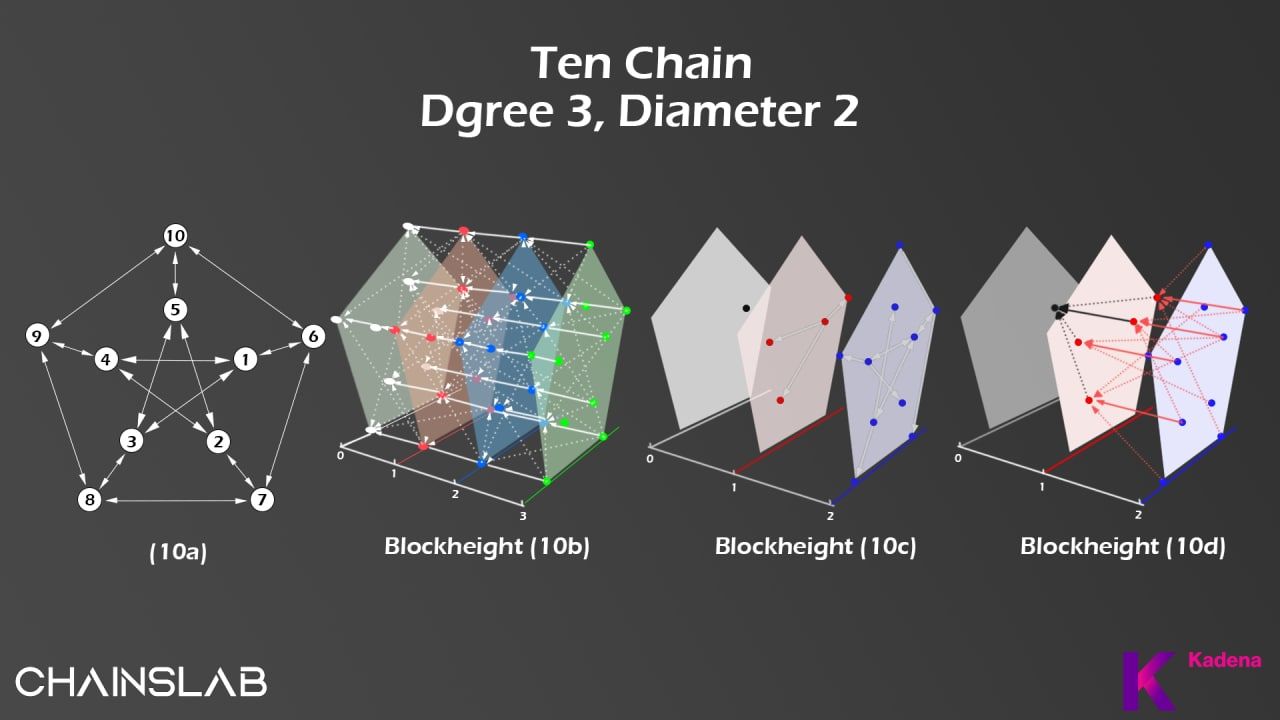
Kadena has core technologies, which are important conditions that will make PoW on Kadena different from other blockchains. Those features are Chainweb, Pact and Kuro.
ChainWeb
The architecture of the project is called ChainWeb and as mentioned earlier, it is based on the combination of multiple blockchain “Bitcoin-like” acting in parallel in order to execute network transactions and mined at the same time on a single network. Each of the PoW chains are in charge of mining the same coin and contains references to the previous block of its counterpart chains, so they have the capacity and power to validate each other’s transactions and share liquidity. In this operation, each individual chain has the same capabilities as the main chain.
The ChainWeb is designed with the sole objective of streamlining transactions in a linear fashion while adding new parallel chains to the main network. It works on two key phenomenons called “sharding” and “braiding”.
- Sharding indicates the splitting of one blockchain into several unique chains.
- Braiding means the mechanism where each block in a peer chain has references to the hash of the preceding blocks from different peer chains.
In simple words, ChainWeb is a linked bundle of numerous parallel chains known as “peer chains” that all function together for the same network at the same time. In there, public blockchain is a network of Proof of Work systems running on top of ChainWeb that provides information security and high throughputs.
On the miner side, miners are directed to each chain individually, reducing the typical bottleneck that we usually find in currencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. Thanks to its new design, high transaction throughput is enabled at the base layer without the need to implement new scalability or functionality solutions at the second layer. The entire operation is geared towards optimizing its base layer to transaction performance and achieving greater developer adoption without implementing second-layer functionality or scalability solutions.
After you have grasped some of the advantages of Kadena's mechanism with Chainweb, now let's check again the current problem of blockchains mentioned at the beginning of the section and find out how Kadena can solve it.
- Scalability: each shard is only concerned with a limited fraction of transactions in the entire blockchain. It aids in the scalability of the blockchain. Hence, this results in high throughput.
- Security: when it comes to securing these chains, the braiding feature helps protect the network due to each block in the network having the hash of its previous block as well as the hash of previous blocks in other peer chains inside the network. This feature lets each block, independent of which shard or chain it comes from, to validate other blocks in the network.
Pact
As introduced in its internal testing, according to the team, it does not have any transaction limits per second. This is due to Kadena’s native smart contract language, Pact. This language makes it possible to ameliorate common flaws observed in Ethereum’s Solidity, most notably the language’s susceptibility to infinite loops and lack of formal verification.
Another feature of Pact is that its smart contracts can be updated at a moment’s notice without the need for a hard fork. The language was created to be readable by humans and verified by computers.
Pact and ChainWeb together is a powerful combination that allows developers and businesses to use a public blockchain in a safe, secure, and stable way that they know they’ll be able to trust. Smart contracts should be useful, human readable, and verified to behave as intended, and a public blockchain should be fast, stable, and capable of handling the throughput necessary for real applications.
Kuro
On its own, Kadena’s permissioned blockchain delivers scalability and usability beyond any other private blockchain today. Private blockchain is a closed blockchain, only authorized people can participate in validation of the network (through mining or holding coins, depending on the consensus mechanism of the blockchain). And often new businesses have the need to use this private blockchain.
Kadena’s private blockchain uses a “Byzantine Fault Tolerant” (BFT) consensus protocol. BFT refers to the ability for a network (a group of computers) to continue working in the face of breakdowns or errors. As part of the Kadena hybrid blockchain ecosystem running the smart contract language Pact and with integration to our public blockchain, Kadena’s private blockchain becomes even more powerful. Here are a few of the additional features and benefits that only Kadena can provide to the private blockchain market:
- Automatic bug detection through formal verification.
- Human-readable code that is accessible to programmers and executives alike.
- Flexibility to upgrade smart contract terms to reflect changing business needs.
- Easy integration to existing enterprise databases with a native API.
- Advanced security options like key rotation and pluggable encryption allow you to dial up security to meet specs.
Kadena Limitations
Kadena can scale to meet the needs of its users, but the scaling isn’t automatic. Initially, the main limitation to scaling is adoption. The public blockchain will hard-fork to higher throughput configurations, but each hard-fork needs to be motivated by alleviating congestion as the upgrade to a larger network requires miners to procure more replicating servers. To upgrade from a 50-chain to 100-chain network, the 50-chain network needs to be congested and demonstrating continued adoption. Long-term, bandwidth becomes the main resource that is constrained.
Besides, the fact that the network uses the PoW mechanism to mine coins will also have many controversies that have happened with Bitcoin or other PoW users on the issue of cost and energy consumption.
V. Economic Security
The Kadena Chain Relay provides economic security through bonded KDA for Ethereum, Cosmos and Polkadot decentralized bridges. The Kadena bridge accepts and validates block headers from other blockchain platforms like Ethereum. To do so, it needs a way to accumulate assurance around the headers in the form of endorsements from actors that have something to lose if the data is faulty.
Consider a DAI token on Ethereum. To wrap it onto the Kadena, DAI is deposited in a smart wallet on Ethereum. This deposit is captured in a cryptographic proof and presented to a smart contract on Kadena, which must verify that the deposit occurred in order to issue the matching amount of wrapped DAI onto Kadena. To do this, the smart contract relies on the Chain Relay to validate that the block header referenced in the supplied proof exists on Ethereum. Thus, the Chain Relay provides a critical service as an attesting authority for block headers from the bridged chain.
To validate headers, participants lock up KDA to become bonders. Bonders propose headers from the bridged chain, after which a random selection of bonders can endorse the proposed header. With enough endorsements, a header is valid and can be used to validate proofs.
At launch, relay bonds are purchased for a fixed amount of KDA. To become a bonder, a participant must put up 50,000 KDA to be locked up for 30 days. During this time, the bonder participates in the chain relay, proposing and endorsing headers using the relay software. In return, they accrue fees both for endorsing headers (activity fees) as well as a fee for locking up the bond (risk fees).
VI. Tokenomics and Metrics
Tokenomics
Kadena's native token is used to pay for computing power on the blockchain (i.e., the execution of smart contracts and transactions), equivalent to the function of gas on Ethereum. It is also used to reward miners for discovering the next valid block. In short, the use cases for KDA tokens consist of:
- Direct transfers between users (payments).
- The creation of new smart contracts.
- Paying the gas cost of executing smart contracts.
Token Metrics
Kadena held two private token sales in early 2018 in the form of a Simple Agreement for Future Tokens (SAFT). The first round was closed in January 2018, totaling $2.25 million by offloading 4.5 million KDA ($0.50 per KDA). The second was secured in April 2018 and brought in another $12.9 million through the sale of 17.2 million coins ($0.75 per KDA).
Mining rewards will also face a “halving” event, where the amount of coins awarded to miners per block decreases by half. This system models itself after Bitcoin, which has a halving event about every four years and is designed to eventually make the coin deflationary. As for ongoing inflation, the block reward started at about 2.3 KDA per block at genesis. This amount will decrease by roughly 0.3% every 87,600 blocks until block height #95,308,800 when the mining reward stagnates at 0.1 KDA per block. The block reward will eventually drop to zero at block height #125,538,057.
More important is that all of the coins are already fully distributed to all investors including SAFT A & B, and CoinList public sale. A majority of KDA is mainly reserved for miners as rewards for facilitating transactions on its blockchain. According to Kadena’s block explorer, there are currently around 198 million KDA circulating and the estimated emission rate of $KDA is 48 million coins per year.
Thus, it can be seen that the internal selling pressure is almost gone, apart of the platform share is used to pay salaries and operating expenses. This will be a favorable condition for the platform's price growth in the future when there is no longer selling pressure from early investment funds.
VII. Team & Partners
Kadena has one of the most experienced and intelligent teams from the world’s leading companies like JPMorgan, Google, Microsoft, Apple, etc. The project was founded by Stuart Popejoy and Will Martino, who were Ex-employees of JPMorgan and the SEC’s crypto committee. They also built JPMorgan’s first blockchain known as JPM Coin and later they introduced Kadena blockchain.
One more thing needs to know is Kadena’s advisor team consists of experts such as Dr.Stuart Haber, the co-inventor of blockchain and the most cited author in Satoshi Nakamoto’s renowned 2008 Bitcoin White Paper.
Kadena has previously raised $15M from some of the most respected funds in crypto out of 16 investors through 3 funding rounds.
VIII. Conclusion
Kadena intends to give corporate and startup blockchain solutions that have the security of Bitcoin, almost no gas expenses, and fast throughput. Furthermore, it employs the Pact smart contract language, which is intended to be more user-friendly than other programming languages.
Kadena is a project with a solid foundation in both technology and finance, having a founding team with many years of experience in the blockchain industry and having contributed to leading technology and financial corporations in the US. That is why in the past year, combined with the development of the crypto market, KDA price has increased rapidly 90x from $0.31 to $29 in just over 3 months.
Although the controversy about energy consumption still revolves around coins using the PoW mechanism, they are still considered as good pieces of cake. Especially, Kadena receives great support from the community and other businesses. Recently, on September 13, BITMAIN - the world's leading manufacturer of cryptocurrency mining servers, announced the sale of the KDA Miner KA3.
#ANTMINER #KA3 delivers:
— BITMAIN (@BITMAINtech) September 13, 2022
✅Extraordinary hashrate performance of 166T
✅New industry standard of 19J/T, pioneering into a new era of energy savings and optimized performance
✅Most advanced air-cooling heat dissipation technology
ZOOM in now: 966 4307 2084 pic.twitter.com/6egmOr1O3A
Objectively speaking, Kadena is receiving a lot of beneficial information, promoting the development of the ecosystem and expanding the model. Furthermore, there is no longer selling pressure from early investors, and the increase in KDA price in the near future is certain to happen and deserves to be considered in the investment portfolio.
