I. Market Context
Trading, a primitive of all financial arrangements, has historically been enabled by intermediating exchanges. That form factor largely carried over unchanged to today’s cryptocurrency markets that is until the concept of a decentralized exchange (DEX) was realized.
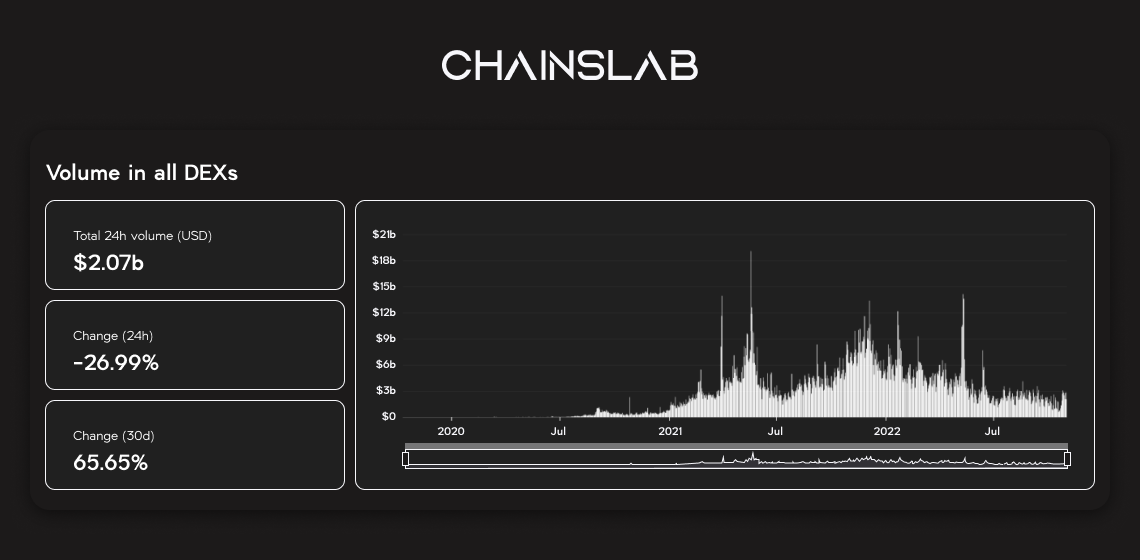
Now, these disruptive market-making models exhibit broad ecosystem adoption and continue attracting significant month-over-month volume growth. It is therefore of no surprise that the pace of innovation in DeFi continues to be led by the segment. As we look forward, appreciating the direction that developers are pushing these avant-garde trading models requires a brief review of the industry’s current state.
DeFi is supposed to remove barriers and inefficiencies. So why is it so much more expensive to trade on DeFi than on centralized exchanges?
This context then leads to a perspective on Hashflow, a project innovating on liquidity architectures and one that we think has the potential to enhance the value delivered to end users through a more calibrated approach to asset price discovery.
II. What Is Hashflow?
As an introduction from the team, Hashflow is a decentralized exchange designed for interoperability, zero slippage and MEV-protected trades. Hashflow is currently available on 7 networks: Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, zkSync 2.0, Optimism and Arbitrum, and has crossed $10B in trading volume since launch in 2021. Non EVM-chains are in deployment like Solana, Aptos, Sui, etc.
Hashflow protocol employs a request-for-quote (RFQ) model popularized by traditional over-the-counter (OTC) trading, served by professional market makers, and merges that with a Web 3 “vending machine experience” like front-end. The team tries to decouple decentralized trading’s reliance on an algorithmic pricing regime and shift those decisions to expert humans that could apply their powerful off–chain models to improve pricing.
III. What Makes Hashflow Unique?
A Hybrid Solution
Most DEXes rely on automated market makers (AMMs) to enable the exchanging of assets, and although important, they’re far from perfect. Why could we say that? AMMs model is really inefficient in capital, routinely prone to risks like sandwich attacks and impermanent loss, and cannot price non-spot assets.
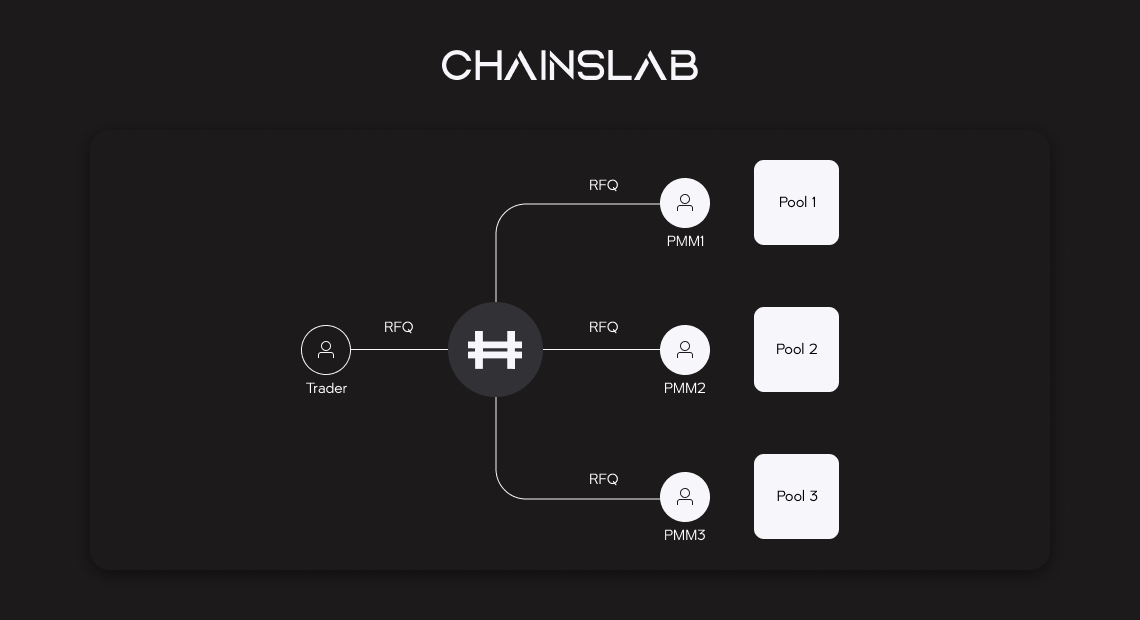
What is request-for-quote? A request-for-quote is a standard financial process whereby suppliers are invited/requested to start a bidding process, leaving to bidding on specific services and products. More detailed specifications about the asset will result in a more reliable demand factor. Quote trading will involve investors requesting quotes on spreads offered, commission/transaction fees and prices.
Back to Hashflow, by using a RFQ model to allow professional market makers to manage liquidity pools, the protocol solves these issues. In turn, traders and liquidity providers (LPs) gain access to enhanced efficiency, security, and products previously impossible in DeFi.
In other words, a hybrid approach, where institutional-grade market makers with deep experience in efficiently managing capital, like CEXes, are aggregated to provide automated quotes through a permissionless front-end whereby users benefit from lower trading fees and retain the security of on-chain settlement and self-managed custody of DEXes.
Bridgeless Cross-Chain Swap
Vitalik, Ethereum’s founder, used to state that “the future will be multi-chain, not cross-chain”. There are so many proven reasons why this is so. We have observed too many cross-chain bridge hacks, due to its vulnerability. The most recent is BNB Chain's $566M hack.
But now, cross-chain asset trading will no longer worry about that. Hashflow does not require users to escrow their assets to mint wrapped assets on the destination chain. Instead, Hashflow allows users to swap natively across chains without the need for a bridge. Hashflow currently uses LayerZero for validation but the contracts are designed to be modular and can plug into any generalized message passing system.
In addition, an advantage of bridgeless cross-chain swap is gas and transaction fees efficiency. The issues of using AMMs model are that execution price is not guaranteed, MEV protection is missing, and slippage risk is high. Using an AMM in conjunction with a bridge must be a gas “nightmare”.
Furthermore, the users have to pay a fee across two different chains as well as the relayers and validators to enable smooth cross-chain communication. As reported, it costs approximately 270k gas units on each side to enable a cross-chain swap on Hashflow, which is significantly 5x lower compared to other cross-chain swap with bridge, which cost over 1M gas units.
Lastly, most chains take anywhere between 3-6 or even 15-20 minutes to swap cross-chain. With a bridgeless mechanism, users do not need much time, every trade could be instantly executed.
Hashverse
With the Hashverse, the project introduces a gamified, storyverse-driven governance structure that operates with a vote-escrowed token model and engages stakers. Hashflow aims to upend the traditional governance approach of DAOs and introduce a model where veHFT stakers create an in-game character. With this gamified approach, users can complete tasks that benefit the community and earn rewards in the process, all the while staying engaged in the governance process.
IV. Hashflow vs CEXes & DEXes
We take a deeper look at how Hashflow stacks up against decentralized and centralized peers across the addressed properties below.
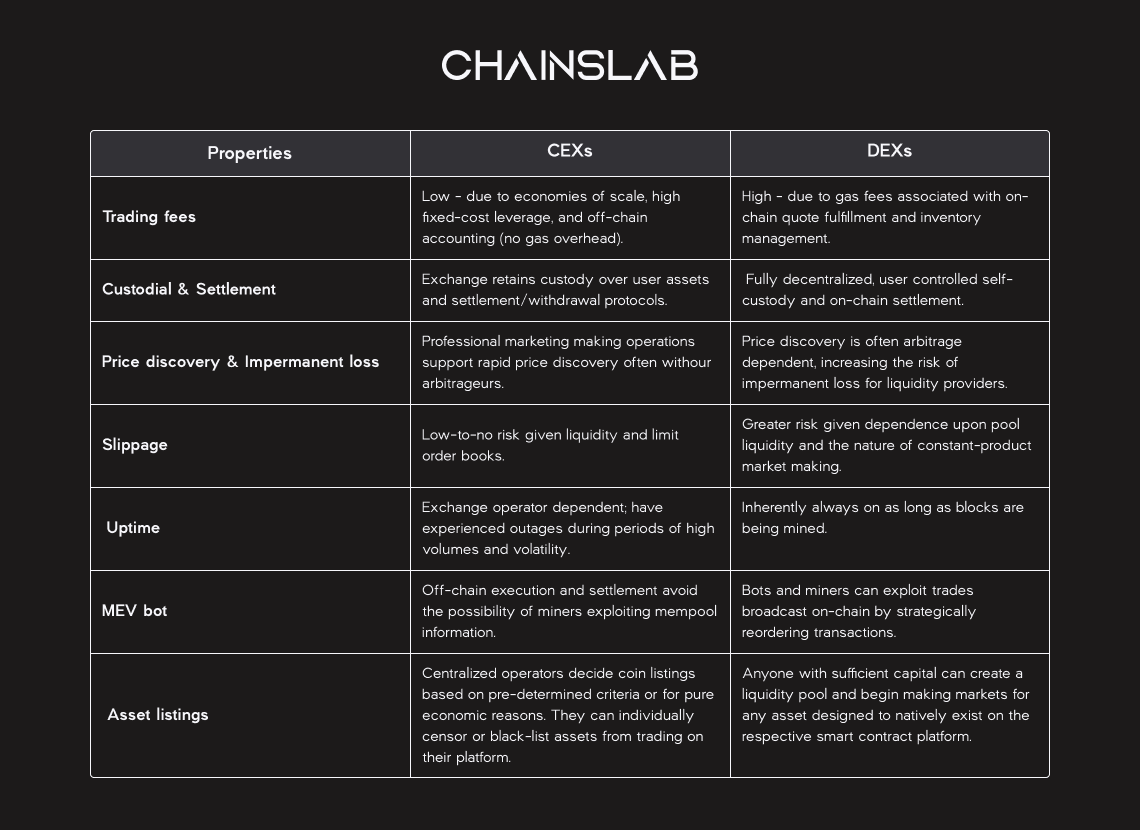
Hashflow vs CEX
Relative to centralized operators, Hashflow’s model retains the benefits of user-controlled custody and on-chain settlement. When a quote is accepted, the market makers will broadcast the signed transaction to the network, and assets are subsequently exchanged between the user’s wallet and the market maker’s pools through Hashflow smart contract. As a result, users still have a self-custodial feature, the same system as DEXes.
Despite outsourcing market making to professional traders who have full discretion over their market participation, Hashflow was thoughtfully designed to retain the “always-on” uptime characteristic of the blockchain ecosystems they serve. The team integrated trade routing to existing DEXes for cases where inferior quotes are offered by the platform’s own market makers.
This backstop feature, therefore, allows Hashflow to retain the power of a fully decentralized exchange during severe market events or situations where censorship may present itself. While perhaps not intended, it also preempts attempts to aggregate Hashflow’s RFQ service. Furthermore, since anyone can theoretically become a market maker on Hashflow, the platform retains the benefit of permissionless asset listing that DEXes uniquely offer to projects and users.
Hashflow vs DEX
Hashflow market makers, who will be deploying proprietary quantitative trading systems capable of considering alternative systems to compute prices off-chain and more efficiently manage capital, should logically be capable of serving quotes that carry lower trading fees than Layer 1 on-chain execution as they avoid the cost overhead and volatility of gas. We can expect to have competitive trading fees, even compared to CEXes. However, we do expect continued DEX innovation on Layer 2 scaling solutions, to have a more competitive environment.
Speaking of the price discovery model, high-frequency off-chain data can be analyzed and integrated into the quotes of market makers pools, based on their preferred management strategy. When scaled to multiple market makers standing ready to serve quotes, competition for trading volume should quickly bring prices in line with the broader market, benefiting users and enabling a more resilient market liquidity.
Hashflow’s model gives market makers far more granular control over their inventory, meaning significantly less capital required to operate against standard AMM liquidity pools, lower risk of impermanent loss and arbitrage. Therefore, the hybrid solution of Hashflow is likely to draw disproportionate volumes for more naturally volatile assets, derivatives trading, e.g., options/perpetual swaps, where the DeFi still not be exposed much.
Furthermore, by implementing the RFQ model, end-users face no slippage risk. The approach of “signature-based” pricing, users take quotes directly from market makers and then have full discretion overfilling a standing offer or otherwise letting it expire, facing no exposure to the intermediate volatility over the decision period. In other words, once a price is accepted, the order gets submitted on-chain as offered. The RFQ model is also inherently MEV-resistant for traders since once a discrete quote is accepted.
V. Team & Backers
Hashflow was launched by CEO Varun Kumar, a San Francisco-based blockchain entrepreneur with a PhD in aeronautics and astronautics from Stanford University. He previously worked for the German Aerospace Center and NASA. CTO Victor Ionescu is a Romanian tech specialist with a computer science degree from Oxford. He previously worked at Airbnb, Facebook and Google.
$3,200,000 was raised in the Seed Round on April 2021, funded by Dragonfly Capital, Electric Capital, Alameda Research, Galaxy Digital, IDEO Colab Ventures, Arrington Capital, LedgerPrime, Gumi Cryptos and Morningstar Ventures with an average price of $0.02.
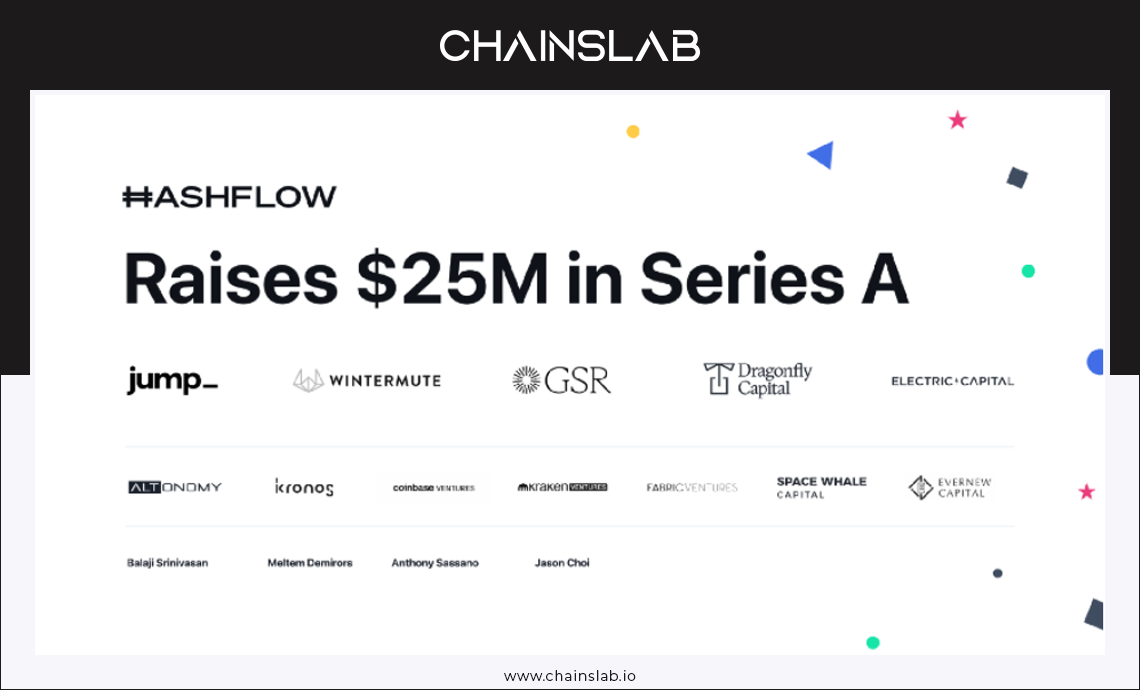
In addition, Hashflow closed its Series A funding round in July 2022, raising $25 million from Jump Crypto, Wintermute Trading, GSR, Kronos Research and Altonomy. Other investors include Coinbase Ventures, Kraken Ventures, Fabric Ventures, Evernew Capital, Spacewhale Capital, and angel investors Meltem Demirors, Anthony Sassano, Tatiana Koffman and Jason Choi.
VI. HFT Tokenomics & Metrics
Tokenomics
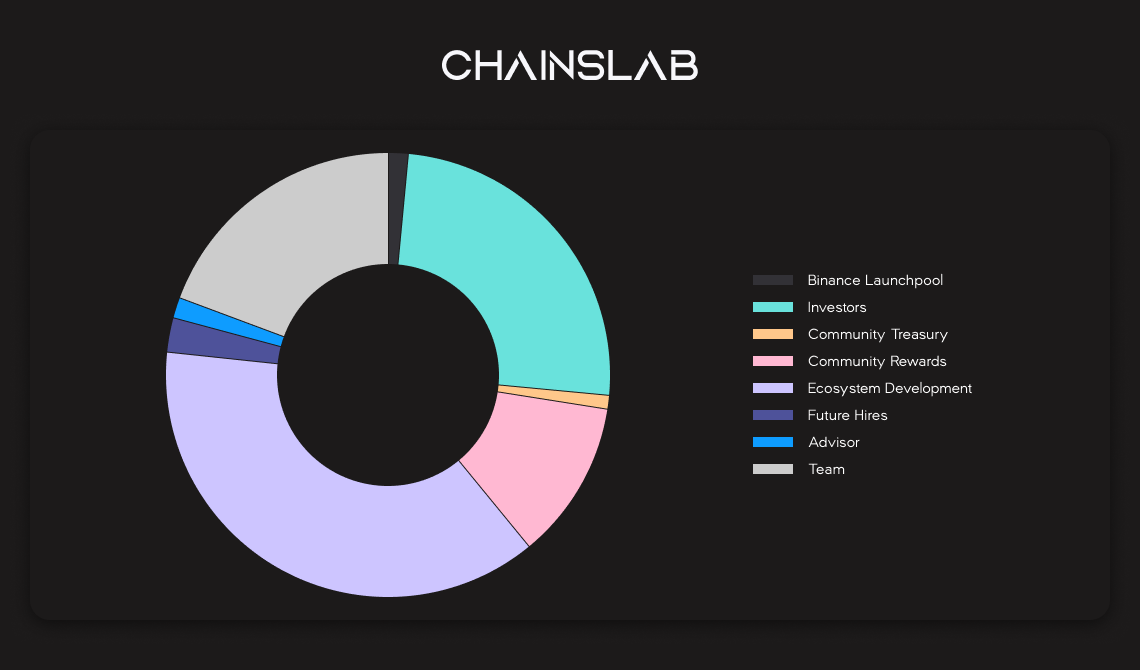
The total HFT supply is 1 billion tokens. HFT is the native token for Hashflow protocol as well as the Hashverse. The protocol intends to deploy a ve-token (vote-escrowed token) model which would allow HFT holders to stake their tokens for a specified period of time in exchange for the ability to participate in governance.
Users can stake HFT to unlock features within the ecosystem:
- Governance: Hashflow governance will follow a vote-escrow (ve) token model where voting rights are determined based on the amount of HFT staked as well as the duration for which HFT is locked. Staking tokens will grant users the right to vote and manage the future of the protocol. This includes decisions relating to protocol fees, marketing, and code development.
- In-DAO Health & Rewards: staked tokens will be used to determine users’ health metrics within the Hashverse. Users must continuously adjust the amount and duration of their staked tokens in order to maintain their health within the Hashverse. The protocol will continue to reward the most active members of the community and their Hashverse presence will play a major role in redeeming these rewards.
Token Metrics
The initial circulating supply when listed on exchanges, as reported, is 175,229,156 HFT, equivalent 17.52% total supply. The project has raised a total $28.2M from three rounds of private token sales, with 25% of the token supply sold. The latest funding round was $400M in valuation. If we translate this $400M valuation to a potential floor FDV, this would be $70M in initial market cap, $0.4 per token. $70M is quite an acceptable number in this market condition, while the total crypto market cap is coming back to $1 trillion.
Currently, 15 million HFT is farming on Binance Launchpool. Taking into comparison to the previous listing on Binance, a layer 1 blockchain Aptos with a $4B valuation of the latest funding round, which is 10x more than HFT. Of course, comparing a trading protocol versus a layer 1 blockchain is not fair, just count the number only. With the similar market condition of Aptos launch, we can expect Hashflow to do the same or higher. As the author estimated, the launch on November 07, HFT could be dumped by tokens allocated to early contributors but not much. Then we can find the price to fly at least 3x to around $1.2 - $1.5 to 10x to around $4.
VII. Concluding Thoughts
Hashflow, mentioned earlier, a CeFi and DeFi hybridization, and bridges professional market makers’ pricing strategies on-chain are unique selling points. Hashflow market makers reallocate capital exactly where it is needed instead of fumbling with on-chain ticks. This is appealing particularly for LPs, who need not manually manage their positions or entrust a smart contract, rather they can leverage professional market makers like Wintermute, Jump Trading, Alameda, LedgerPrime, Galaxy Digital and a lot more to come. We’ll continue to see more examples of established players and standards entering DeFi, and building hybrid protocols.
Official Links
Website: https://www.hashflow.com/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/hashflow
Discord: https://discord.com/invite/hashflow
Telegram: https://t.me/hashflownetwork
